Some acids are safe enough that even a homeowner can use them, like . It’s designed to be used as a household cleaner, as long as you follow the directions and all safety precautions. Some other acids are simply too caustic and corrosive for anyone to handle.
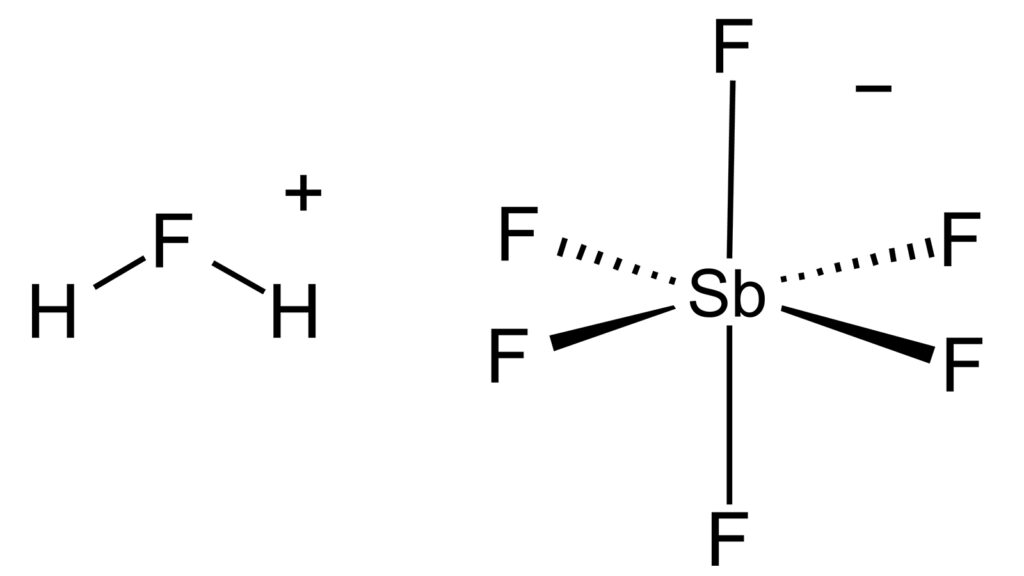
So what happens when you mix two of those? You get something altogether stronger. For instance, when equal amounts of the acids hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5) are combined, the results are too remarkable to ignore. Advertisement You don’t get just any other acid.
You end up with the , or , known to humankind: fluoroantimonic acid, aka HSbF . Fluoroantimonic acid is a colorless liquid that emits a toxic vapor. Swallowing or inhaling it can be fatal, and skin contact? Think severe burns.
It stands tall in the superacid category, a group of strong acids with acidic strength surpassing that of . Given its potency, we can’t use the regular pH or pKA scales to measure its strength. Here, the , denoted as H, steals the spotlight.
Advertisement Fluoroantimonic acid registers an H of -21, while sulfuric acid’s H measures -12. To translate that, fluoroantimonic acid is a staggering 20 × 10¹⁹ times . If this were a showdown, it would like Captain Marvel squaring off against a newborn kitten.
Hydrogen Fluoride and Hydrogen Ions This is the backbone of our champion, fluoroantimonic acid. Hydrogen ions make a substance acidic, and the higher the concentration, the more potent the acid. Hydrogen fluoride, on its own, isn’t the strongest acid, but it is a key component of some very strong ones.
Advertisement Despite its overwhelming strength, fluoroantimonic acid has an Achilles’ heel: It can’t erode , commonly known as Teflon. Thus, Teflon containers are the chosen vessels to store this potent liquid. Another storing method is within a hydrofluoric acid solution, where our record holder doesn’t undergo explosive decomposition.
Advertisement Beware, though — this acid will dissolve glass, most plastics and every organic compound. It even reacts explosively with water. It’s most definitely not a school science experiment.
It demands respect, best left to seasoned chemists and experts in organic chemistry. Advertisement Fluoroantimonic acid’s unique talent is protonation — it donates protons to organic compounds. This alters the compound’s properties like mass, solubility and hydrophilicity.
Such a trait is invaluable to chemists, aiding in chemical reactions, etching glass, refining gasoline and even crafting explosives. While it holds the title of the world’s strongest acid, hydrofluoric acid is riskier due to its presence in common products, making accidental exposure likelier. Advertisement For those brave enough to work with superacids, personal protective equipment, including respirators and protective eyewear, is non-negotiable.
It’s the modern chemist’s armor against a substance that can dissolve flesh and bones in a blink. The chemical realm is vast, and while fluoroantimonic acid has its revered status, there’s an array of other fascinating acids that deserve a mention. Let’s explore the unique attributes of these acids, diving into their strengths, weaknesses and roles in various processes.
Carborane Acids These are among the strongest of the strong acids, next only to fluoroantimonic acid. Their unique molecular structure, backed by the American Chemical Society’s research, helps them maintain their potency. Advertisement What sets them apart is their weak bond with hydrogen ions, making them less corrosive than fluoroantimonic acid.
Magic Acid It sounds fantastical, but magic acid is very real! It’s formed by mixing fluorosulfuric acid (HSO₃F) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF₅). This acid completely dissociates in an aqueous solution, releasing a high concentration of hydrogen ions. Nitric Acid, Phosphoric Acid and Perchloric Acid These are examples of strong acids that completely dissociate when dissolved in water.
While they may not match the extreme acidity of fluoroantimonic acid, they’re essential in industries, ranging from fertilizer production to rocket propellant. Benzoic Acid and Oxalic Acid These weak acids don’t completely dissociate in water. However, they play crucial roles in our daily lives, from food preservation to cleaning agents.
Hydronium Ion All acids, when dissolved in water, produce this positively charged ion. It’s the real culprit behind the acidic properties of a solution. “Ways to destroy iPhones” is an entertaining genre on YouTube.
Whether they’re smashed with a hammer or dissolved with chemicals like gallium, bromine or fluoroantimonic acid, citizen scientists use a range of methods to put the durability of modern tech to the test. Advertisement.
From: howstuffworks
URL: https://science.howstuffworks.com/fluoroantimonic-superacid.htm